WASM-4 是一款使用 WebAssembly 实现的复古风格游戏机。凹语言作为国内首个面向 WebAssembly 设计的通用编程语言在 syscall/wasm4 内置标准库对 WASM4 平台提供了支持,从而为使用凹语言开发小游戏的用户提供最佳体验。
我们以一个简单的乒乓球游戏作为例子,看看如何开发 WASM4 游戏。
安装凹语言 v0.15 以上的版本,或者通过以下 Go 命令安装最新的 wa 命令行:
$ go install wa-lang.org/wa@master
然后通过以下命令创建一个 hello 新目录工程:
$ wa init -wasm4
$ tree hello/
hello/
├── README.md
├── src
│ └── main.wa
└── wa.mod
2 directories, 3 files
命令行环境进入 hello 目录后,输入wa run可以在浏览器打开查看效果。
直接修改src/main.wa文件:
import (
"math/rand"
"strconv"
"syscall/wasm4"
)
const (
width = 5
height = 15
ballSize = 5
screenSize = int(wasm4.SCREEN_SIZE)
)
// 玩家 1(右边): 上下方向键
// 玩家 2(左边): ED 键对应上下键, 左右方向键盘控制
global game = NewPongGame(true) // 双人游戏
#wa:export update
func Update {
game.Input()
game.Update()
game.Draw()
}
Update 函数会以每秒 60 帧的频率被调用,其中分布出来游戏的输入、更新游戏状态并显示。
在对象中保存的游戏状态:
// 游戏的状态
type PongGame :struct {
isMultiplayer: bool // 多人游戏
ballX: int // 球的水平位置
ballY: int // 球的竖直位置
dirX: int // 球的方向
dirY: int // 球的方向
y1: int // 左边挡板位置
y2: int // 右边挡板位置
score1: int // 玩家分数
score2: int // 玩家分数
}
// 构建一个新游戏对象
func NewPongGame(enableMultiplayer: bool) => *PongGame {
return &PongGame{
isMultiplayer: enableMultiplayer,
ballX: screenSize / 2,
ballY: screenSize / 2,
dirX: 1,
dirY: 1,
y1: screenSize / 2,
y2: screenSize / 2,
score1: 0,
score2: 0,
}
}
主要是乒乓球、挡板等位置和方向信息。
通过不同方向键盘分别控制 2 个挡板的移动。
func PongGame.Input {
// 第 1 个玩家
if pad := wasm4.GetGamePad1(); pad&wasm4.BUTTON_UP != 0 && this.y1 > 0 {
this.y1 -= 2
} else if pad&wasm4.BUTTON_DOWN != 0 && this.y1+height < screenSize {
this.y1 += 2
}
// 第 2 个玩家或机器人
if this.isMultiplayer {
// 左右方向键盘控制
if pad := wasm4.GetGamePad1(); pad&wasm4.BUTTON_LEFT != 0 && this.y2 > 0 {
this.y2 -= 2
} else if pad&wasm4.BUTTON_RIGHT != 0 && this.y2+height < screenSize {
this.y2 += 2
}
if pad := wasm4.GetGamePad2(); pad&wasm4.BUTTON_UP != 0 && this.y2 > 0 {
this.y2 -= 2
} else if pad&wasm4.BUTTON_DOWN != 0 && this.y2+height < screenSize {
this.y2 += 2
}
} else {
this.y2 = this.ballY // 自动对齐到接球位置(TODO: 失误机制)
}
}
根据键盘更新挡板的位置信息。
每秒钟 60 帧的速度更新状态:
func PongGame.Update {
// 更新球的方向
if dirNow := this.paddleCollision(); dirNow != 0 {
wasm4.Tone(2000, 5, 100, wasm4.TONE_PULSE2|wasm4.TONE_MODE2)
if rand.Int()%2 != 0 {
this.dirX = dirNow
this.dirY = -1
} else {
this.dirX = dirNow
this.dirY = 1
}
}
// 更新球的位置
this.ballX += this.dirX
this.ballY += this.dirY
// 检查球是否反弹
if this.ballY > screenSize || this.ballY < 0 {
wasm4.Tone(2000, 5, 100, wasm4.TONE_PULSE2|wasm4.TONE_MODE2)
this.dirY = -this.dirY
}
// 判断得分
if this.ballX <= 0 || this.ballX > screenSize {
wasm4.Tone(1000, 5, 100, wasm4.TONE_PULSE2|wasm4.TONE_MODE2)
if this.ballX <= 0 { // 左边玩家失球
this.score2 += 1
} else if this.ballX > screenSize {
this.score1 += 1 // 右边玩家失球
}
// 重置球位置
this.ballX = screenSize / 2
this.ballY = screenSize / 2
this.dirX = -this.dirX
}
}
同时判断失球和得分情况。以下是碰撞判断:
func PongGame.paddleCollision => int {
if this.ballX < width &&
this.ballY < this.y2+height &&
this.ballY+ballSize > this.y2 {
return 1
}
if this.ballX+ballSize > screenSize-width &&
this.ballY < this.y1+height &&
this.ballY+ballSize > this.y1 {
return -1
}
return 0
}
球碰到和超出边界表示失球得分。
WASM4 的调色板寄存器一次只能存储 4 种颜色,可以通过更改这一寄存器来引入新的颜色。以下是 WASM4 默认的配色表:
WASM4 内置的绘图函数不直接访问这个颜色表寄存器,而是访问同样能够存储 4 个颜色的 DRAW_COLORS 寄存器来指定对应的颜色表索引。可以通过wasm4.SetDrawColors函数完成。
绘制场景的代码:
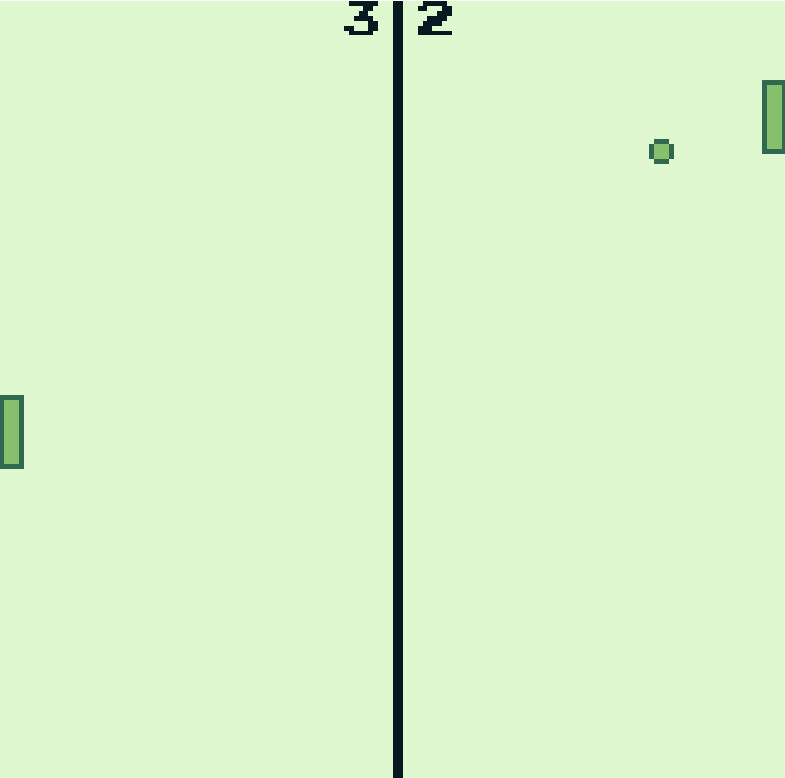
func PongGame.Draw {
wasm4.SetDrawColors(0, 4)
wasm4.SetDrawColors(1, 0)
wasm4.Text(strconv.Itoa(this.score1), 85, 0)
wasm4.Text(strconv.Itoa(this.score2), 70, 0)
wasm4.Rect(screenSize/2, 0, 2, screenSize)
wasm4.SetDrawColors(0, 2)
wasm4.SetDrawColors(1, 3)
wasm4.Oval(this.ballX, this.ballY, ballSize, ballSize)
wasm4.Rect(0, this.y2, width, height)
wasm4.Rect(screenSize-width, this.y1, width, height)
}
到此乒乓球游戏就完成了。
完整代码大约 150 行: https://github.com/wa-lang/wa/tree/master/waroot/examples/w4-pong
在线体验地址: https://wa-lang.org/wa/w4-pong/
如果你也是游戏爱好者,也可以试试用凹语言开发自己的游戏了。
这是一个专为移动设备优化的页面(即为了让你能够在 Google 搜索结果里秒开这个页面),如果你希望参与 V2EX 社区的讨论,你可以继续到 V2EX 上打开本讨论主题的完整版本。
V2EX 是创意工作者们的社区,是一个分享自己正在做的有趣事物、交流想法,可以遇见新朋友甚至新机会的地方。
V2EX is a community of developers, designers and creative people.