更多精彩内容,请关注微信公众号:后端技术小屋
说明:STL 采用 SGI 版本, 下载地址
stl_alloc.h
alloc.h
STL 中默认使用的内存分配器,被广泛用于vector, hashmap, deque等数据结构中
该类实现以下接口:
_Tp* allocate(size_type __n, const void* = 0) {
return __n != 0 ? static_cast<_Tp*>(_Alloc::allocate(__n * sizeof(_Tp)))
: 0;
}
// __p is not permitted to be a null pointer.
void deallocate(pointer __p, size_type __n)
{ _Alloc::deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof(_Tp)); }
void construct(pointer __p, const _Tp& __val) { new(__p) _Tp(__val); }
void destroy(pointer __p) { __p->~_Tp(); }
alloc
allocator申请和释放内存通过alloc中的静态方法实现。
class allocator {
typedef alloc _Alloc; // The underlying allocator.
}
而alloc定义如下,其实是__default_alloc_template 的一个特化类
typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, 0> alloc;
而__default_alloc_template由一级内存池和二级内存池组成
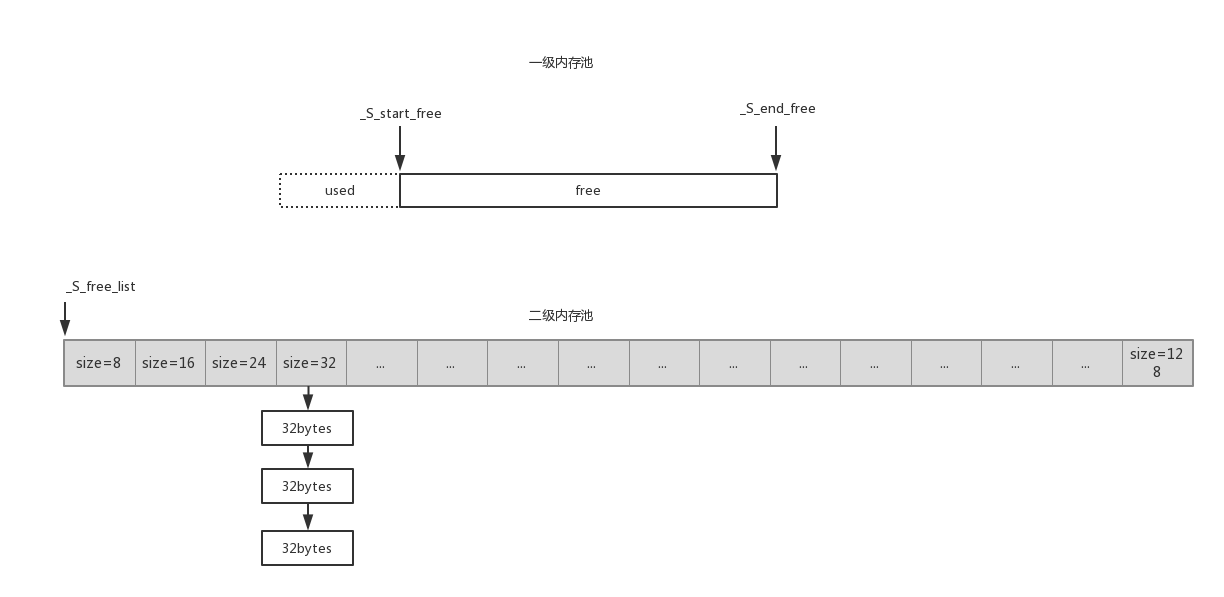
二级内存池为一个静态数组,数组元素类型为_Obj*,每个数组元素即一个单向链表的头。
_S_free_list存储不同大小空闲内存块的链表头,如size为 8 的chunk_list的链表头为_S_free_list的第一个元素,size 为 16 的chunk_list对应第二个元素,以此类推
private:
# if defined(__SUNPRO_CC) || defined(__GNUC__) || defined(__HP_aCC)
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[];
// Specifying a size results in duplicate def for 4.1
# else
static _Obj* __STL_VOLATILE _S_free_list[_NFREELISTS];
_Obj类型:
union _Obj {
union _Obj* _M_free_list_link;
char _M_client_data[1]; /* The client sees this. */
};
一级内存池是一段连续的大缓冲区。其中_S_start_free表示可用内存开头,_S_end_free表示可用内存末尾, _S_heap_size统计所有堆上分配内存的大小总和。
// Chunk allocation state.
static char* _S_start_free;
static char* _S_end_free;
static size_t _S_heap_size;
对于 size 不超过最大_MAX_BYTES(128)的内存分配请求,尽量从二级内存池中分配:
size大小找到二级内存池中对应的 slot, 并获取空闲内存块链表的头,取出第一个内存块,并将其从链表中删除size大小找到二级内存池中对应的 slot, 将需要释放的内存块插入到空闲内存块组成的链表的头部,并更新对应 slot 中的指针。因此,使用__default_alloc_template申请内存的总体流程如下:
size是否超过最大_MAX_BYTES(128)malloc_alloc::allocate从堆上申请内存;size大小索引到相应的空闲内存块链表,判断是否为空二级内存池中的分配策略20*size大小的内存,判断可用一级内存池的大小(即left_bytes)left_bytes >= 20*size, 直接从从一级内存池分配left_bytes >= size, 从一级内存池分配尽量多的size, 一部分用于内存分配,一部分用于放入二级内存池left_bytes < size, 首先将一级内存池中剩余内存块插入到二级内存池中,然后通过malloc申请2 * __total_bytes + _S_round_up(_S_heap_size >> 4)大小的内存,作为一级内存池。最后再跳转到 6,返回可用内存地址,返回当__default_alloc_template的执行 allocate 和 deallocate 时,都会针对一级内存池和二级内存池进行动态调整,因此 STL 中通过互斥锁保护这些临界资源
// It would be nice to use _STL_auto_lock here. But we
// don't need the NULL check. And we do need a test whether
// threads have actually been started.
class _Lock;
friend class _Lock;
class _Lock {
public:
_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; }
~_Lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; }
};
而__NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK和__NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK是这样定义的
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ _S_node_allocator_lock._M_acquire_lock(); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ _S_node_allocator_lock._M_release_lock(); }
互斥锁又是怎么实现的呢?根据不同的平台有多种实现方式。其中之一便是使用 linux 下的 pthread lib
pthread_mutex_t _M_lock;
void _M_initialize() { pthread_mutex_init(&_M_lock, NULL); }
void _M_acquire_lock() { pthread_mutex_lock(&_M_lock); }
void _M_release_lock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&_M_lock); }
simple_alloc,debug_alloc 这两者同alloctor相似,不同点在于前三者将实际的内存分配器作为一个模板参数传入类中,然后调用其进行内存分配和释放。而后者内部直接使用alloc, 即__default_alloc_template<true, 0>
主要用于 STL 哈希表和红黑树中节点的分配
模板参数中,_Tp表示元素类型,_Alloc表示实际的内存分配器
template<class _Tp, class _Alloc>
class simple_alloc {
public:
static _Tp* allocate(size_t __n)
{ return 0 == __n ? 0 : (_Tp*) _Alloc::allocate(__n * sizeof (_Tp)); }
static _Tp* allocate(void)
{ return (_Tp*) _Alloc::allocate(sizeof (_Tp)); }
static void deallocate(_Tp* __p, size_t __n)
{ if (0 != __n) _Alloc::deallocate(__p, __n * sizeof (_Tp)); }
static void deallocate(_Tp* __p)
{ _Alloc::deallocate(__p, sizeof (_Tp)); }
};
debug_alloc: 元素类型默认为 char, 内存分配器通过模板参数指定 debug_alloc 实现中有一个比较有意思的地方:
buf_len(8 Byte) | buf(n Byte)
// Allocator adaptor to check size arguments for debugging.
// Reports errors using assert. Checking can be disabled with
// NDEBUG, but it's far better to just use the underlying allocator
// instead when no checking is desired.
// There is some evidence that this can confuse Purify.
template <class _Alloc>
class debug_alloc {
private:
enum {_S_extra = 8}; // Size of space used to store size. Note
// that this must be large enough to preserve
// alignment.
public:
static void* allocate(size_t __n)
{
char* __result = (char*)_Alloc::allocate(__n + (int) _S_extra);
*(size_t*)__result = __n;
return __result + (int) _S_extra;
}
static void deallocate(void* __p, size_t __n)
{
char* __real_p = (char*)__p - (int) _S_extra;
assert(*(size_t*)__real_p == __n);
_Alloc::deallocate(__real_p, __n + (int) _S_extra);
}
static void* reallocate(void* __p, size_t __old_sz, size_t __new_sz)
{
char* __real_p = (char*)__p - (int) _S_extra;
assert(*(size_t*)__real_p == __old_sz);
char* __result = (char*)
_Alloc::reallocate(__real_p, __old_sz + (int) _S_extra,
__new_sz + (int) _S_extra);
*(size_t*)__result = __new_sz;
return __result + (int) _S_extra;
}
};
推荐阅读
更多精彩内容,请扫码关注微信公众号:后端技术小屋。如果觉得文章对你有帮助的话,请多多分享、转发、在看。
这是一个专为移动设备优化的页面(即为了让你能够在 Google 搜索结果里秒开这个页面),如果你希望参与 V2EX 社区的讨论,你可以继续到 V2EX 上打开本讨论主题的完整版本。
V2EX 是创意工作者们的社区,是一个分享自己正在做的有趣事物、交流想法,可以遇见新朋友甚至新机会的地方。
V2EX is a community of developers, designers and creative people.